An exception is an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program i.e at run time, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions.
Error vs Exception
Error: An Error indicates serious problem that a reasonable application should not try to catch.
Exception: Exception indicates conditions that a reasonable application might try to catch.
Exception: Exception indicates conditions that a reasonable application might try to catch.
Exception Handling in JavaIn this page, we will learn about Java exceptions, its type and the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions. What is Exception in JavaDictionary Meaning: Exception is an abnormal condition.What is Exception HandlingException Handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors such as ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, RemoteException, etc.Advantage of Exception HandlingThe core advantage of exception handling is to maintain the normal flow of the application. An exception normally disrupts the normal flow of the application that is why we use exception handling. Let's take a scenario:Hierarchy of Java Exception classesThe java.lang.Throwable class is the root class of Java Exception hierarchy which is inherited by two subclasses: Exception and Error. A hierarchy of Java Exception classes are given below: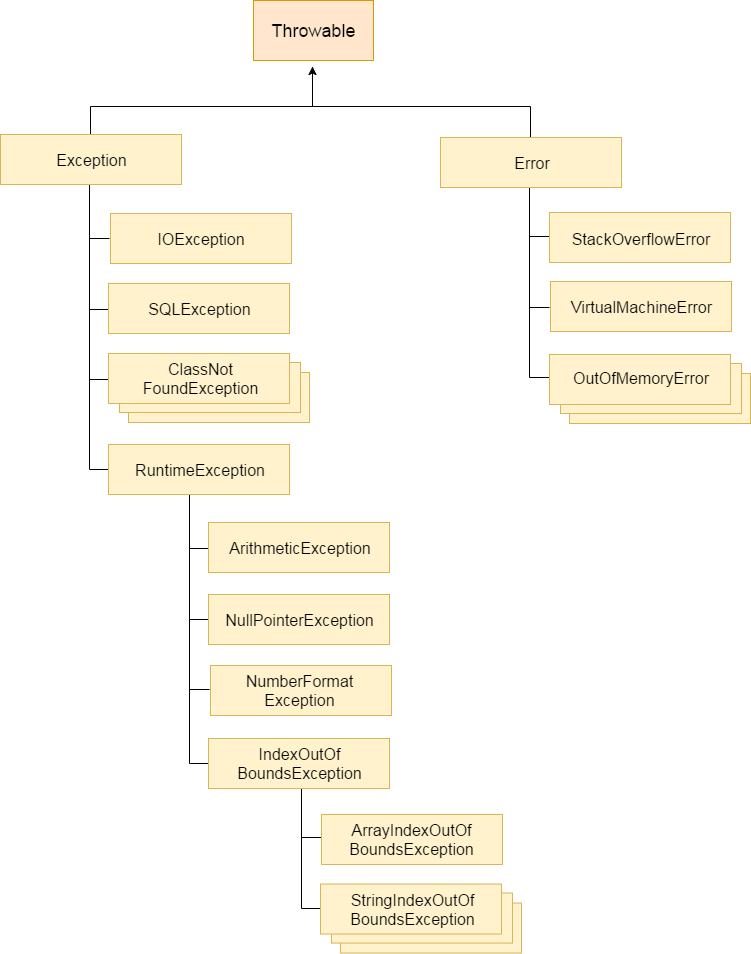 Types of Java ExceptionsThere are mainly two types of exceptions: checked and unchecked. Here, an error is considered as the unchecked exception. According to Oracle, there are three types of exceptions:
1) Checked ExceptionThe classes which directly inherit Throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as checked exceptions e.g. IOException, SQLException etc. Checked exceptions are checked at compile-time.2) Unchecked ExceptionThe classes which inherit RuntimeException are known as unchecked exceptions e.g. ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException etc. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time, but they are checked at runtime.3) ErrorError is irrecoverable e.g. OutOfMemoryError, VirtualMachineError, AssertionError etc.
|
finally block:
package com.cerotid.exceptionhandling;
public class FinallyBlockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
System.out.println("try");
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("catch");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}

No comments:
Post a Comment